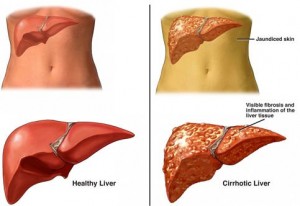
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that attacks the liver and causes it inflammation. Hepatitis C is one of several hepatitis viruses and is typically considered to be among the most serious of them.
Hepatitis C- Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Nausea or poor appetite
- Muscle and joint pains
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
How is it and not spread.
Hepatitis C is spread or passed through contact with an infected person’s blood, most commonly through accidental needle sticks or needles shared during illegal drug use. Since hepatitis C is spread through blood, the following precautions are advised:
- Do not share razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, or anything else that could have blood on it.
- Get checked if you received a piercing or tattoo in an unclean environment using unsterile equipment
- Don’t donate blood, organs, tissue, or semen if you have hepatitis C
- Get checked if you were born to a woman with a hepatitis C
- Get checked if you had a blood transfusion before or organ transplant before 1992
It is NOT spread through:
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Hugging
- Kissing
- Breastfeeding (unless nipples are cracked or bleeding)
- Sharing utensils or glasses
- Casual contact
- Sharing food and water
Everyday contact is not risky. “The transmission rate between people in a household is probably just a little above zero,” says Howard J. Worman, MD, associate professor of medicine at Columbia University’s College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York.
If you think you may be at risk of hepatitis C, see your family doctor or a general practitioner. Once you’ve been diagnosed with hepatitis C infection, your doctor may recommend you see a specialist.