According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more that one-third of American men and women are overweight. As the number of obesity keeps increasing so does the increase of weight loss surgery procedures. How safe are these procedures, is the risk really worth it?
Weight loss surgery
Also known as bariatric surgery, this is one of the most frequent answers obese people turn to. The number of weight loss procedures in the U.S. has increased from 13,000 in 1998 to 200,000 in 2008, says the American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS).
Bariatric surgery is a series of weight loss procedures that an obese individual can have in order to reduce their food intake, therefore causing them to lose weight.
Types of weigh loss surgery
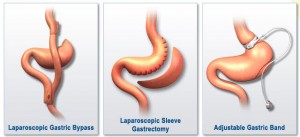
There are three main bariatric surgery procedures used. These are : gastric bypass, gastric banding and sleeve gastrectomy.
1 . Gastric bypass is the most commonly used worldwide, according to the ASMBS. The procedure involves re-routing the digestive system past the stomach in order to promote satiety and suppress hunger.
2 . The gastric band procedure involves having an inflatable band placed around the top portion of the stomach. This creates a smaller stomach pouch, meaning eating less will make a person feel full and satisfy their hunger.
3 . With a sleeve gastrectomy, around 80% of the stomach is removed to create a smaller stomach pouch. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed.
Dr. Elliot Fegelman, medical director for Ethicon, a Johnson & Johnson company that designs and manufactures medical devices, standard diet and exercise strategies only lead to significant weight loss in 5% of the US population.”Surgery for weight loss and control of associated diseases, has been shown to be the most effective option available for patients suffering from obesity and related diseases.”
Obesity can lead to type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and it has also been linked to some cancers, including breast cancer and colon cancer. This condition can seriously damage a person’s quality of life, leaving them immobile and often triggering depression. A person has considered obese if their body mass index (BMI) is over 30. If their BMI is over 40, they are deemed severely obese.